Cracks in Building – Moisture Movement
Preetham Builders one of the Best Builders in Madurai are developing Gated Community Luxury villas and flats.
This gated community ” BRINDAVAN HOMES ” is being developed in Kochadai Madurai, a fast developing area in Madurai.
With abundant water supply and green environments this gated community ” BRINDAVAN HOMES ” with individual buildings and Bungalows present a Resort like feelings.
Preetham Granite M.D addressed the gathering of engineers (Association of Madurai Civil Engineers) on Cracks in Buildings – Causes & Remedies at Hotel Weshtern Park ( 01.09.2016).
Moisture Movement
– Irreversible Movement
– Material undergo some irreversible movement due to initial moisture change
– Reversible Movement
– Material expands on absorbing moisture
– content
– Shrinks on drying
In freshly laid cement concrete pavements and slabs. Sometimes cracks occur before concrete has set due to plastic shrinkage. This happens if concrete surface loses water faster than bleeding action brings it to top. Quick drying of concrete at the surface results shrinkage and as concrete in plastic state cannot resist any tension. Short cracks develop in the material. These cracks mav be 5 to 10cm in depth and their width could be as much as 3mm. once formed these cracks stay and may. Apart from being unsightly affect serviceability of the job.
Hardening process of concrete depends on chemical action of moisture. After mixing and placement moisture contained in the concrete gradually dries out. First moisture present intermolecular space dries out causing some reduction in volume.
Then capillary water is lost as calcium silicate gel crystallizes. This result in shrinkage which is of irreversible of nature.
Most of the cracking in concrete occurs due to shrinkage at the time of initial drying.
With the rise in temperature, fresh concrete expands, but as it is in a plastic state at that stage, very little stress is set up in the material due to this expansion. However, later on, when cooling takes place and concrete has hardened by that time, shrinkage occurs and concrete cracks. Thus heat of hydration in massive structures like dams is an important factor to be contended with. To prevent cracking in such cases, special measures are called for which include use of low-heat cement, use of pozzolanas, pre-cooling of aggregates and mixing water, post-cooling of concrete by circulating refrigerated water through pipes embedded in the body of the concrete, etc.
Initial drying shrinkage due to water loss is irreversible.
Most of the cracks in concrete occurs due to shrinkage at the time of initial drying.
It depends on cement content
higher the cement, higher will be shrinkage.
greater the water cement ratio, greater the shrinkage.
well graded concrete greatly reduces the shrinkage cracks. Concretes having more fines will have greater shrinkages.
Initial drying shrinkage due to water loss is irreversible.
Curing plays very important role in limiting shrinkage.
Curing has to be started as soon as initial set has taken place and to be continued for 7 to 10days.
High humidity and low temperature reduces shrinkage.
Aggregate plays very important role in shrinkage cracks.
Graded aggregates with desired workability will have less shrinkage because of reduction in porosity of hardened concrete
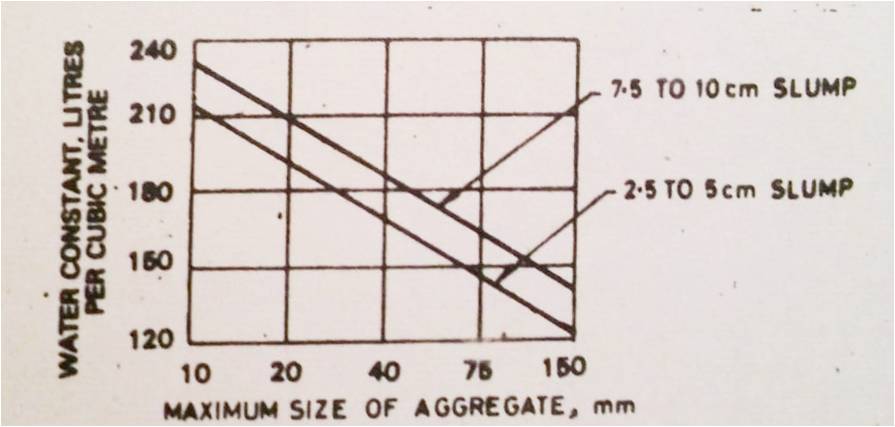
Effect of aggregate size to water requirement of concrete.
Quick drying of concrete at the surface results in shrinkage as concrete in plastic state cannot have any tension.
So surface cracks develop.
These cracks will have 2 to 10 cm in depth and 3mm width.
Once formed these cracks stay and affect the servicability of concrete.